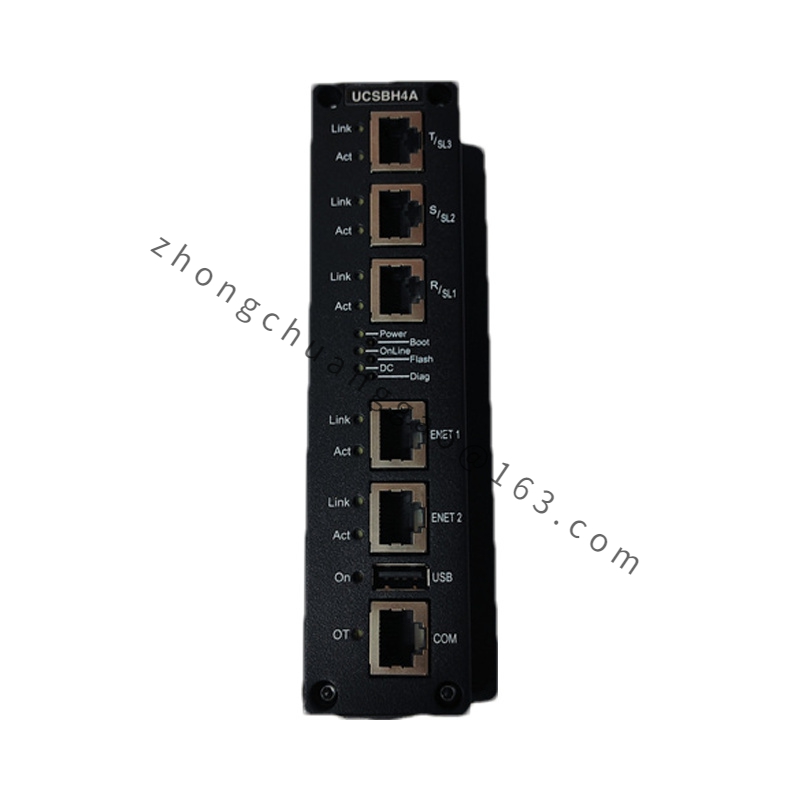
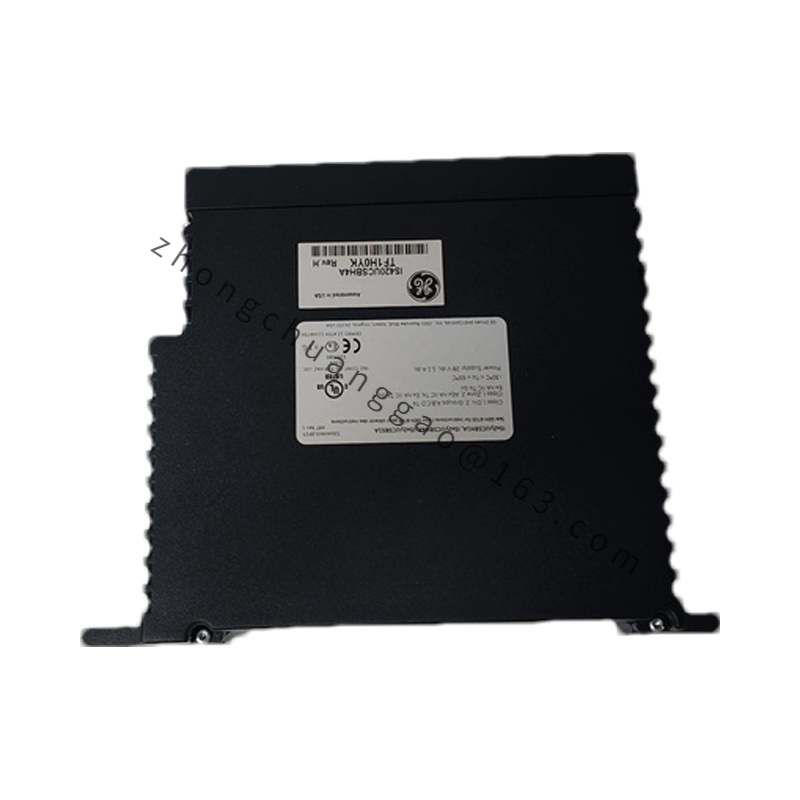
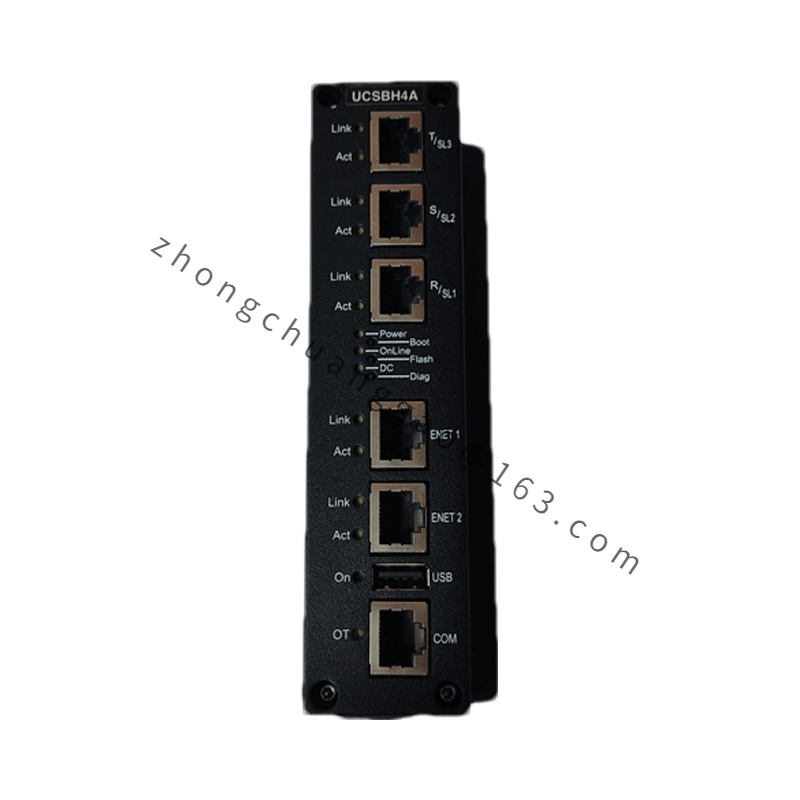
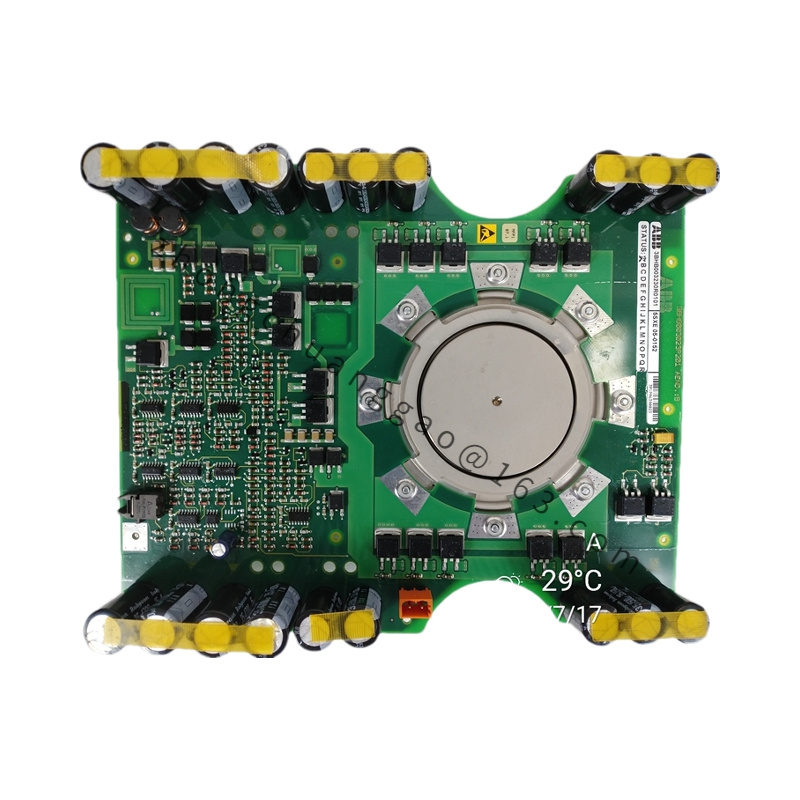
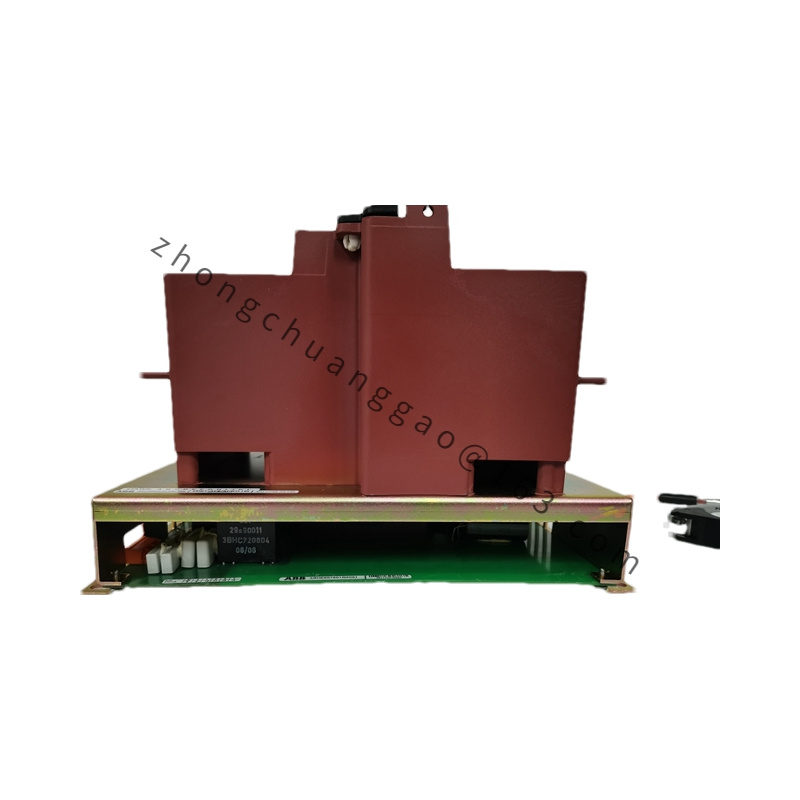
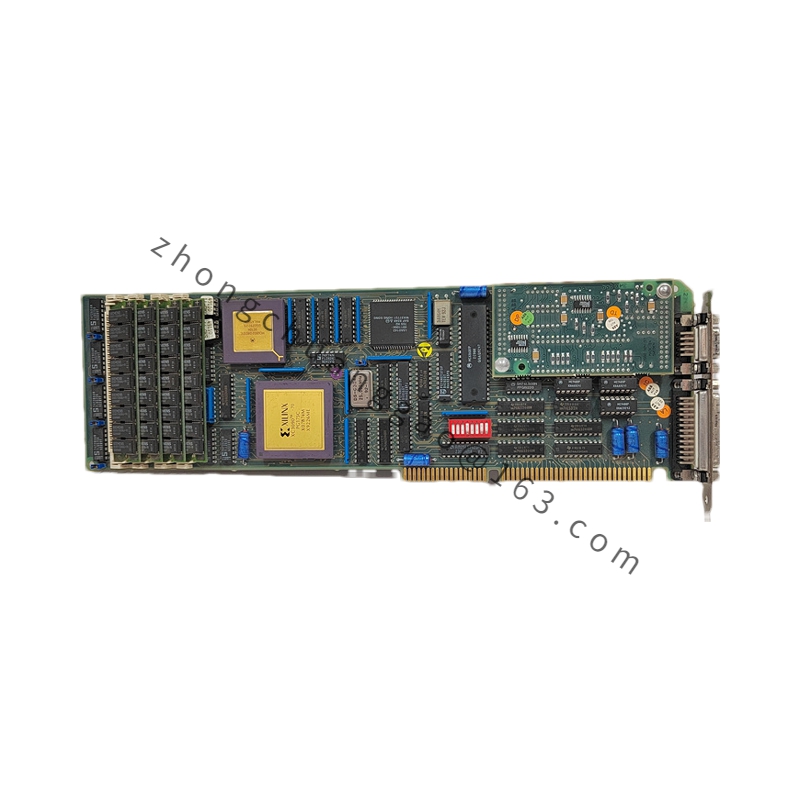
GE IS420UCSBH4A
Technical Specifications
Specification Detail
Model IS420UCSBH4A
Manufacturer General Electric (GE)
Series Mark VIe
CPU 32-bit RISC Processor
Memory 256MB RAM, 512MB Flash
I/O Channels 8 Analog Inputs, 4 Analog Outputs, 8 Digital Inputs, 4 Digital Outputs
Communication Ethernet, RS-485, and IONet (Dedicated Ethernet Network)
Detailed content
Power Supply 24V DC
Power Consumption 20W
Dimensions 225mm x 144mm x 96mm
Weight 2.5 kg
Operating System QNX Neutrino (Real-time multitasking OS)
Functional Features
Advanced Control Technology: The IS420UCSBH4A employs advanced control algorithms for precise and stable control functions, enhancing production efficiency and reliability.
Rugged Industrial Design: Designed for harsh industrial environments, ensuring stable operation in various conditions.
Multi-Channel I/O: Provides a range of analog and digital input/output channels, allowing for monitoring and control of multiple process variables.
Communication Capabilities: Equipped with Ethernet, RS-485, and IONet interfaces for seamless communication with other devices and systems, enabling remote monitoring and data transmission.
Fault Detection: Capable of detecting potential issues or abnormalities in the controlled system, allowing for timely intervention to prevent further damage or safety incidents.
Real-time Operating System: The QNX Neutrino OS provides high-speed and reliable performance essential for industrial applications.
Application Scenarios
Industrial Automation: Commonly used in manufacturing processes, production lines, and equipment control, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
Process Control: Applicable in various process industries, such as chemical, petrochemical, and pharmaceutical, for monitoring and regulating process parameters.
Energy Industry: Deployed in power plants, grid equipment, and other energy production and distribution processes for reliable control and monitoring.
Water Treatment and Environmental Protection: Utilized in water treatment plants and environmental facilities to monitor and control critical parameters like liquid levels and valve statuses.
Transportation Systems: May be employed in traffic control systems to manage signal lights, road signs, and other traffic-related equipment.
Building Automation: Controls lighting, HVAC systems, and security systems in large buildings, enhancing energy efficiency and safety.
Communication Infrastructure: Used in monitoring and controlling communication base station equipment to ensure uninterrupted service.