Detailed content
Technical Specifications
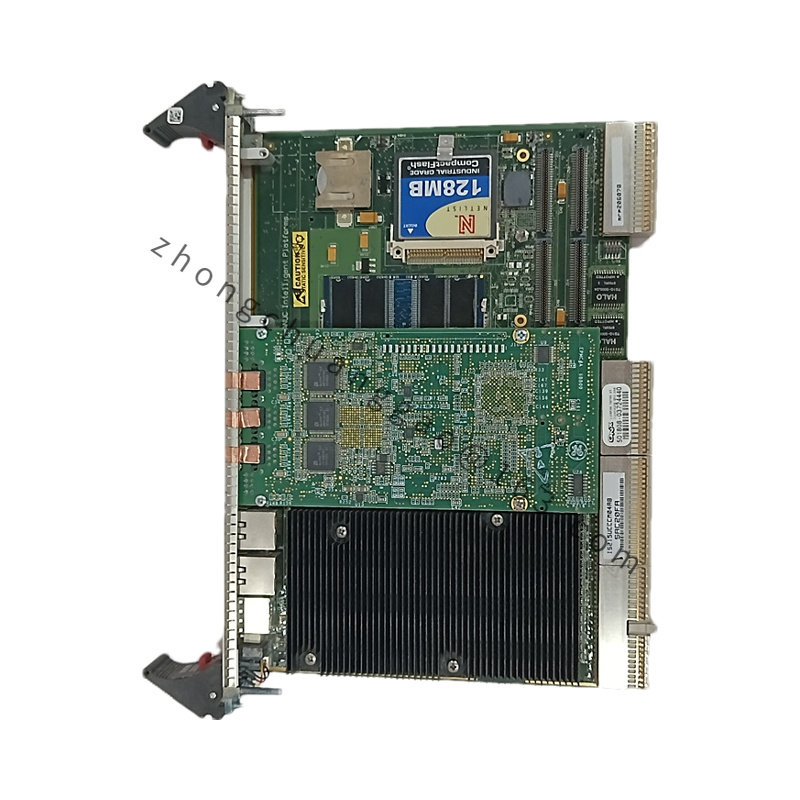
- Model:
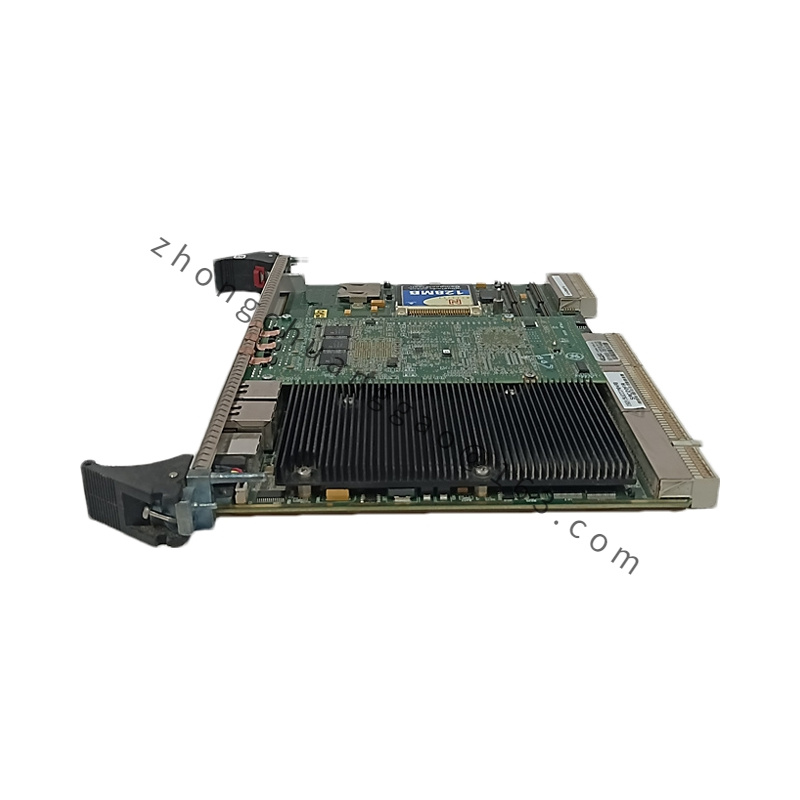
- Model Number: IS215UCCCM04AB
- Type:
- Category: Universal Controller Card (UCC) for GE Mark VIe
- Processor and Memory:
- Processor: High-performance processor for executing complex control algorithms and system tasks.
- Memory: Includes onboard memory for storing configuration settings, system data, and control parameters.
- Input/Output:
- Inputs: Supports a range of digital and analog inputs for interfacing with field devices and sensors.
- Outputs: Provides digital and analog outputs for controlling actuators and external devices.
- Communication Interfaces:
- Ethernet Ports: Multiple Ethernet interfaces for network communication and integration with other system components.
- Serial Ports: Includes serial communication ports for interfacing with additional devices and systems.
- Fieldbus: Supports various fieldbus protocols for integration with field devices and other control systems.
- Power Supply:
- Voltage: Typically operates on a 24V DC power supply; specific requirements should be confirmed with the manufacturer’s documentation.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Operating Temperature: Designed to function within an industrial temperature range, generally from -20°C to +60°C.
- Relative Humidity: Operates effectively in environments with 5% to 95% non-condensing relative humidity.
- Dimensions and Weight:
- Size: Compact form factor suitable for installation in standard control panels or racks.
- Weight: Lightweight to facilitate easy installation and integration.
Features
- High-Performance Control:
- Processing Power: Capable of handling complex control tasks and high-speed data processing.
- Reliability: Engineered for high reliability and robustness in demanding industrial environments.
- Versatile I/O Capabilities:
- Input/Output Flexibility: Provides various digital and analog I/O options for comprehensive interfacing with field devices.
- Configuration: Flexible configuration to support a wide range of industrial applications.
- Communication Interfaces:
- Networking: Includes multiple Ethernet and serial ports for seamless system integration and data exchange.
- Fieldbus Support: Compatible with various fieldbus protocols for connecting with field devices and other control systems.
- User Interface:
- Configuration Tools: Provides software tools for configuration, diagnostics, and system monitoring.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Allows real-time monitoring and control of system performance and status.
- Industrial-Grade Design:
- Durability: Designed to withstand harsh industrial conditions, including temperature extremes, vibrations, and electrical noise.
- Compliance: Meets industry standards for safety, performance, and reliability.
Applications
- Industrial Automation:
- Usage: Used in industrial automation systems to manage and control various processes and equipment.
- Application: Suitable for applications in manufacturing, chemical processing, power generation, and other industrial sectors.
- Process Control:
- Role: Integral to process control systems, providing precise control and monitoring capabilities.
- Integration: Works with other control devices and systems for comprehensive process management.
- Data Acquisition:
- Purpose: Collects and processes data from field devices to support data-driven decision-making.
- Benefits: Enhances system visibility and operational efficiency through accurate and reliable data collection.
- SCADA Systems:
- Application: Used in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems for remote monitoring and control of industrial processes.
- Features: Provides real-time data and control capabilities for operators and engineers.
- Building Automation:
- Usage: Applied in building management systems for controlling HVAC, lighting, and other systems within buildings.
- Advantages: Improves building efficiency and comfort through automated control systems.
Additional Considerations
- Installation and Maintenance: Follow manufacturer guidelines for installation and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Technical Support: For detailed specifications, configuration assistance, and troubleshooting, refer to GE’s official documentation or contact their technical support team.