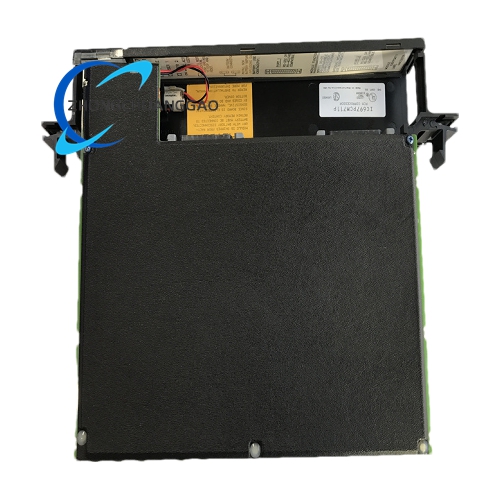
GE IC697PWR724F
Technical Specifications
- Nominal Rated Voltage: 24 volts DC
- Input Voltage Range: 18 to 32 VDC
- Input Power: 160 watts at full load
- Input Inrush Energy: 22 joules maximum
- Output Power: 90 watts maximum
- DC Output:
- +5 VDC: 4.90 to 5.25 volts (5.07 volts nominal), up to 18 amps
- +12 VDC: 11.75 to 12.6 volts, up to 1.5 amps
- -12 VDC: -12.6 to -11.75 volts, up to 1 amp
- Overvoltage Limit:
- +5 VDC output: 5.7 to 6.7 volts
- +12 VDC output: 4 amps maximum
- -12 VDC output: 2 amps maximum
Detailed content
- Overvoltage Limit:
- +5 VDC output: 5.7 to 6.7 volts
- +12 VDC output: 4 amps maximum
- -12 VDC output: 2 amps maximum
- Ride – Through Time: 10 milliseconds minimum at 20 VDC
- Operating Temperature Range: 0 – 60°C
Functional Characteristics
- Multiple Output Voltages: It provides three output voltages (+5 VDC, +12 VDC, -12 VDC) with a total output power of 90 watts, which can meet the power requirements of different components in the industrial automation system.
- Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection: It has built – in overcurrent and overvoltage protection circuits. For example, the overcurrent limit of the +5 VDC output is 26 amps, and when the 5 – V bus voltage exceeds 6.7 V, the output will be clamped to protect the system.
- Dual – Rack Operation: A single power supply can power two racks, provided that the total load is within the appropriate supply rating. The connection to the second rack is achieved through a pre – wired cable (IC697CBL700).
- Easy Installation: The module features an easy – to – use slide – in rack – mount construction, which is convenient for installation and replacement.
Application Scenarios
- Manufacturing Industry: It is used in the automation control systems of production lines as a key control component to realize the control of equipment and the transmission of data.
- Energy Industry: In energy management systems such as smart grids and wind farms, it is used to monitor and control the operating status of equipment to improve energy utilization efficiency.
- Transportation Industry: In transportation control systems such as railways and highways, it is used to realize the control and scheduling of traffic signals to improve the safety and efficiency of transportation.
- Building Engineering: In building automation systems, it is used to control the on – off status of equipment such as lighting and security, improving the intelligent level of building management.