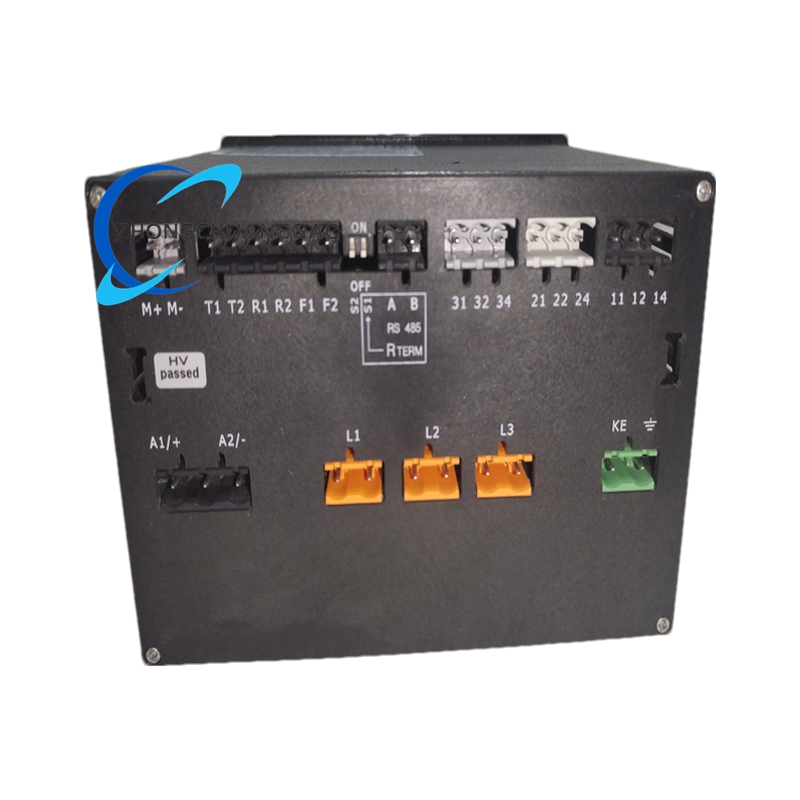
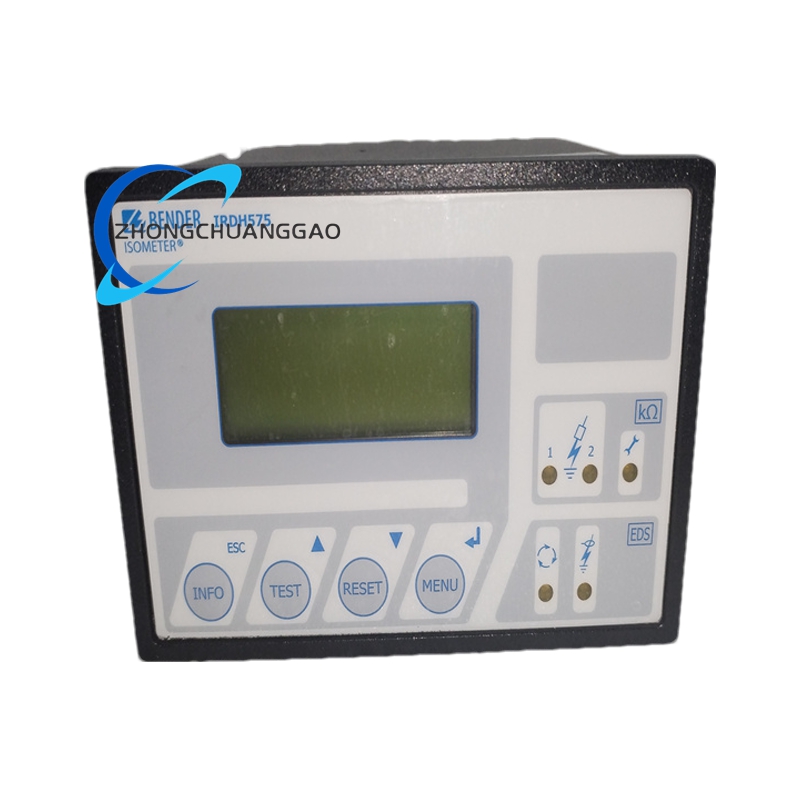
BENDER IRDH575B1W-435
Technical Specifications
- Rated Insulation Voltage: AC 800V
- Rated Impulse Voltage/Pollution Degree: 8kV/3
- Nominal System Voltage: AC, 3/(N)AC 20 – 575V; DC 20 – 575V; AC, 3/(N)AC 340 – 760V; DC 340 – 575V
- Power Supply Voltage: 88 – 264V AC, 42 – 460Hz; DC 19.2 – 72V
- DC Internal Resistance: ≥180k
- Positioning Current DC: 1/2.5/10/25/50 mA
- Operating Temperature Range: -10 – +55°C (working); -40 – +70°C (storage)
- Protection Class: IP30 (internal components); IP20 (terminals); IP40 (for installation door); IP42 (for installation door with sealed panel); IP65 (for installation with transparent front – plate cover)
- Weight: ≤900g
Detailed content
Functional Characteristics
- High – Precision Measurement: Capable of accurately measuring insulation resistance, providing reliable monitoring data.
- High Reliability: Designed for harsh industrial environments to ensure stable system operation.
- Real – Time Monitoring: Can monitor insulation resistance in real – time, promptly detecting insulation faults.
- Rich Alarm Functions: Provides various alarm outputs and indications, facilitating users to handle faults.
- Communication Capability: Supports multiple communication protocols, such as RS485, Ethernet, and Modbus TCP, for easy remote monitoring and control.
- Easy Installation and Maintenance: Adopts DIN rail installation and modular design, making it convenient for users to install and maintain.

Application Scenarios
- Power Systems
- Distribution Networks: Used to monitor low – voltage and medium – voltage distribution systems, promptly detecting ground faults to ensure the reliability of power supply.
- Power Plants: Detects ground faults in the electrical equipment of power plants, preventing equipment damage and shutdown.
- Industrial Automation
- Manufacturing: Monitors the safety of electrical systems in automated production lines and industrial equipment, preventing production interruptions caused by ground faults.
- Chemical Plants: Ensures the safe operation of electrical equipment during chemical production, preventing safety accidents caused by faults.
- Building and Infrastructure
- Commercial Buildings: Monitors ground faults in the electrical systems of large – scale commercial buildings in real – time, ensuring the power safety of buildings.
- Transportation Facilities: Ensures the stability and safety of the power supply system in the electrical systems of subways, airports, and other transportation facilities.
- Medical Facilities
- Hospitals: Monitors ground faults in the medical equipment and power supply systems of hospitals, ensuring the normal operation of medical equipment and the safety of patients.