Detailed content
Technical Specifications
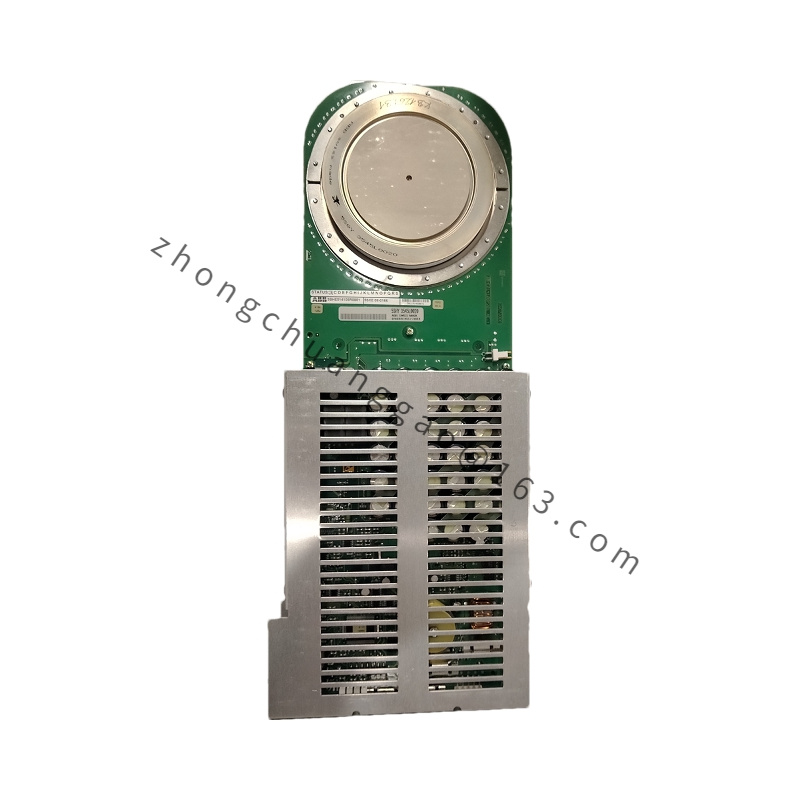
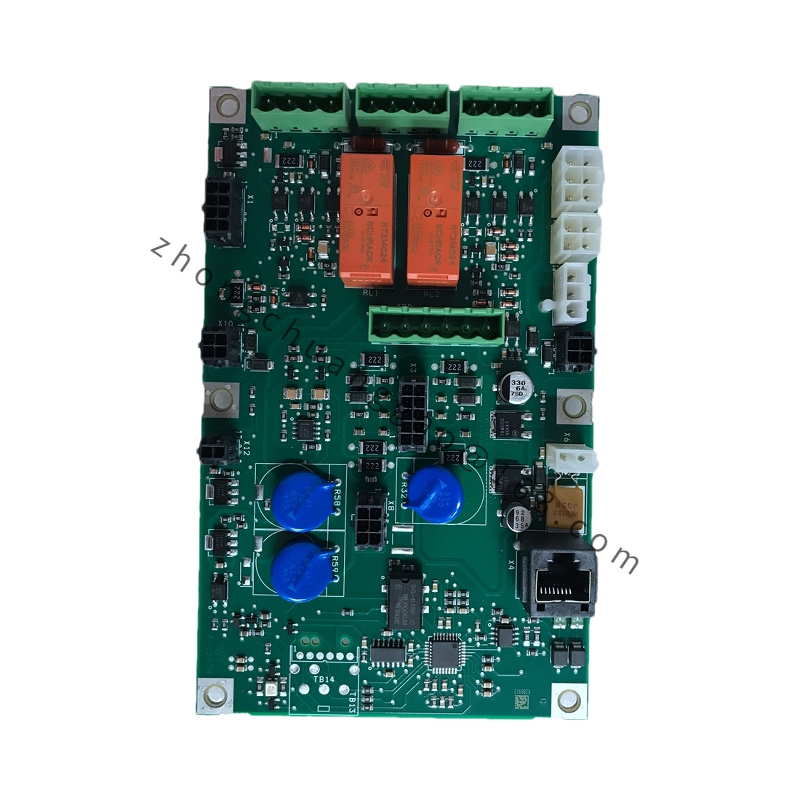
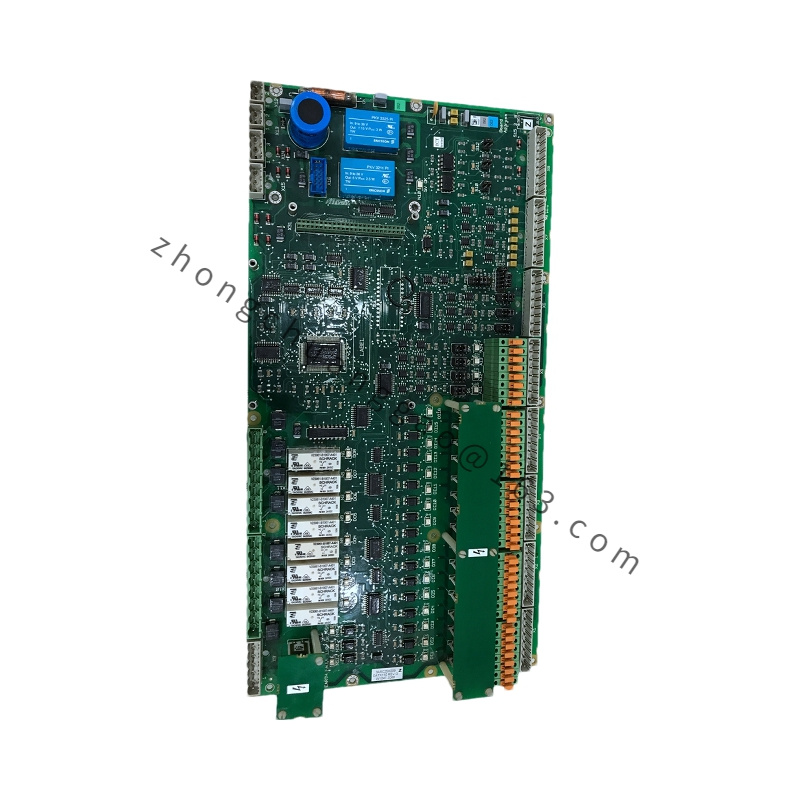
Brand: ABB
Model: PPC905AE101
Input/Output:
Digital Input Points: 10
Rated Voltage: 24V DC, 4mA
Maximum Continuous Allowable Voltage: 30V DC
Surge Voltage: 35V DC, 0.5s
Logic “0” Voltage Range: 5V DC, 1mA
Logic “1” Voltage Range: 15V DC, 1mA
Input Delay: 4.5ms
Signal Input Type: PNP/NPN, Photoelectric Isolation (Field to Logic) 500V AC, 1 minute
Maximum Allowable Leakage Current: 1mA
Cable Length (Shielded): 500m
Cable Length (Unshielded): 300m
Digital Output Points: 6
Output Type: Relay
Output Voltage: 24V DC or 250V AC
Rated Voltage: 5-30V DC / 20-250V AC
Rated Current: 2.0A
Common Terminal Rated Current: 10A
PPC905AE101 Current (Max.): 5A, 4s @ 10% Duty Cycle
Lamp Load: 30W DC / 200W AC
Contact Mechanical Life: 10,000,000
Turn-on Resistance: 0.2Ω
Output Delay: 10ms
Cable Length (Shielded): 500m
Cable Length (Unshielded): 150m
Electrical Parameters:
Bus Consumption Current: 80mA
Total Power Consumption: 3W
Functional Characteristics
Programmability: Allows users to create custom control logic and algorithms to meet specific application requirements.
Multi-Channel Support: With 10 digital input points and 6 digital output points, it can simultaneously monitor and control multiple devices or processes.
Real-Time Control: Capable of performing control tasks in real-time or near real-time conditions to ensure fast and accurate system response.
Communication Interfaces: Typically supports multiple communication interfaces for data exchange and communication with other control devices, sensors, and computers.
Strong Anti-Interference Performance: Ensures stable operation in industrial environments with potential electromagnetic interference.
Industrial Grade Standard: Designed to meet the requirements of industrial environments, with high durability and stability.
Application Scenarios
Industrial Automation: Used in automation systems to control production lines, machine devices, valves, actuators, etc., for automated production and process control.
Process Control: Monitors and controls various process parameters in industries such as chemicals, petrochemicals, and oil and gas, ensuring process stability and safety.
Power System Control: In power systems, it can be used to monitor and control generators, transformers, switchgear, and power distribution systems.
Transportation and Logistics: Controls equipment such as conveyor belts, elevators, lifts, and robots for material handling, sorting, and distribution.
Building Automation: Controls lighting, HVAC systems, security systems, and access control systems in buildings to improve energy efficiency and comfort.
Data Acquisition and Monitoring: Used in data acquisition systems to monitor sensor and instrument data, such as temperature, humidity, and pressure, for real-time monitoring and data recording.








.jpg)
.jpg)