Detailed content
1、 Technical specifications
Manufacturer: ABB (AbbVie), a leading global industrial automation and power technology company.
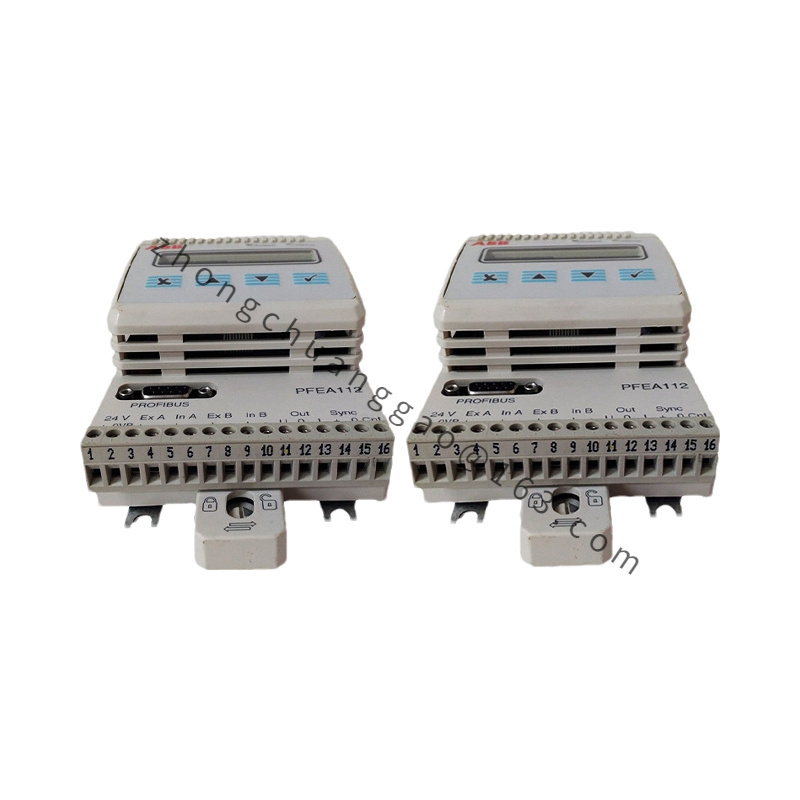
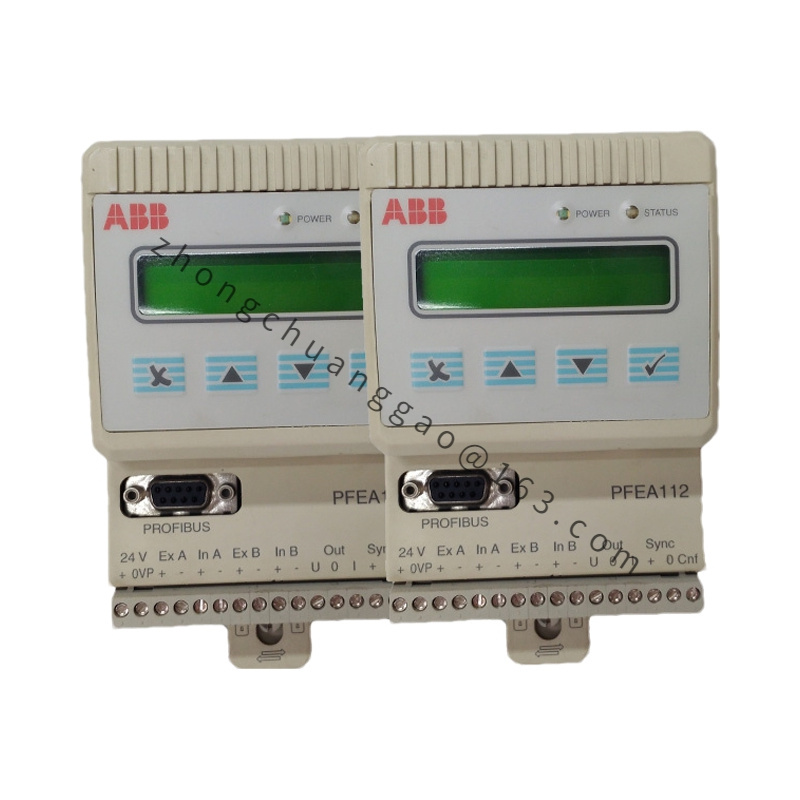
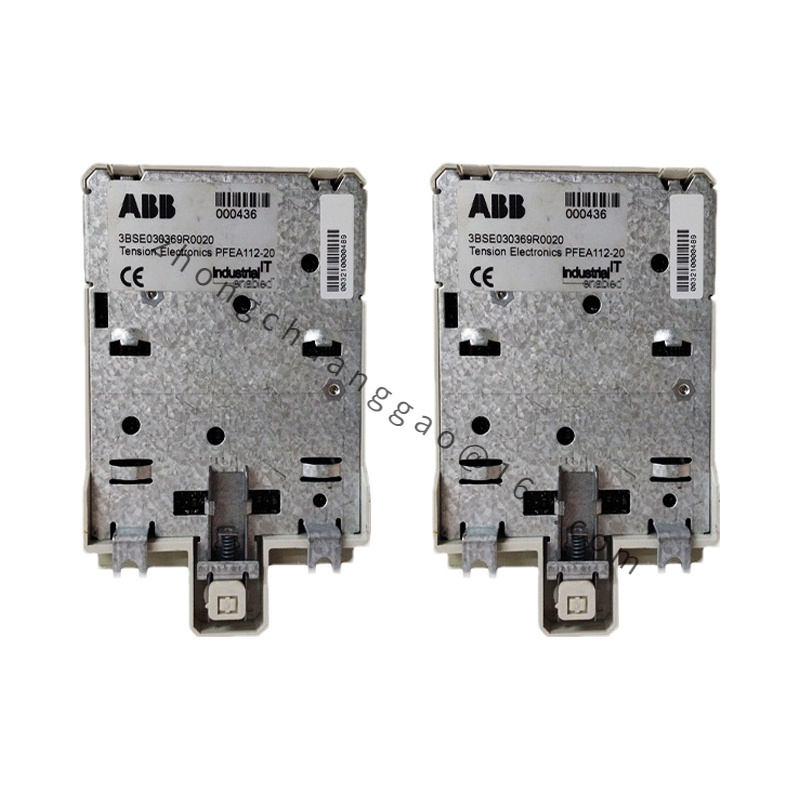
Model: PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020, this model uniquely identifies this specific tension controller.
Communication Interface: Supports multiple communication interfaces such as Ethernet, Modbus, Profibus, etc., facilitating data exchange and integration with other automation devices, control systems, or monitoring systems.
2、 Functional Features
High precision control: Advanced sensors and algorithms are used to achieve high-precision tension control, ensuring the stability and consistency of materials during processing.
Multi channel control: typically equipped with multiple control channels, allowing for simultaneous control of multiple tension devices or winding systems, improving production efficiency.
Easy to program and configure: Provides rich programming interfaces and configuration options, making it convenient for users to program and configure according to specific needs, meeting diverse application requirements.
User friendly interface: Equipped with a user-friendly interface, operators can easily monitor tension status, set parameters, and perform fault diagnosis.
High reliability and stability: Industrial equipment designed for high reliability and stability, capable of long-term stable operation under harsh environmental conditions.
Multiple control modes: Supports multiple control modes, can be flexibly configured according to different production needs, and adapts to various tension control scenarios.
3、 Application scenarios
The ABB PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020 tension controller is widely used in various industrial fields that require precise tension control, including but not limited to:
Printing industry: Ensure stable tension of materials such as paper and film during the printing process to avoid a decrease in printing quality.
Coating industry: During the coating process, control the tension of the material to ensure uniform coating and stable quality.
Textile industry: In textile machinery, controlling the tension of materials such as yarn and fabric to prevent breakage or uneven winding.
Metallurgical industry: In the production and processing of metal strips, the tension of materials is controlled to ensure product quality and processing efficiency.
Packaging industry: In packaging machinery, controlling the tension of packaging materials ensures packaging effectiveness and product quality.
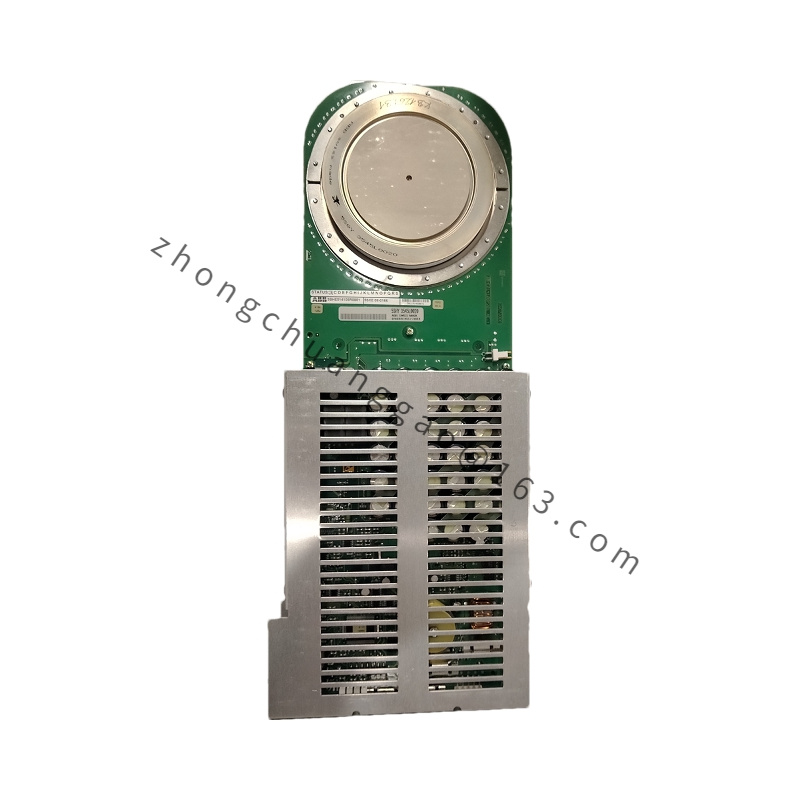
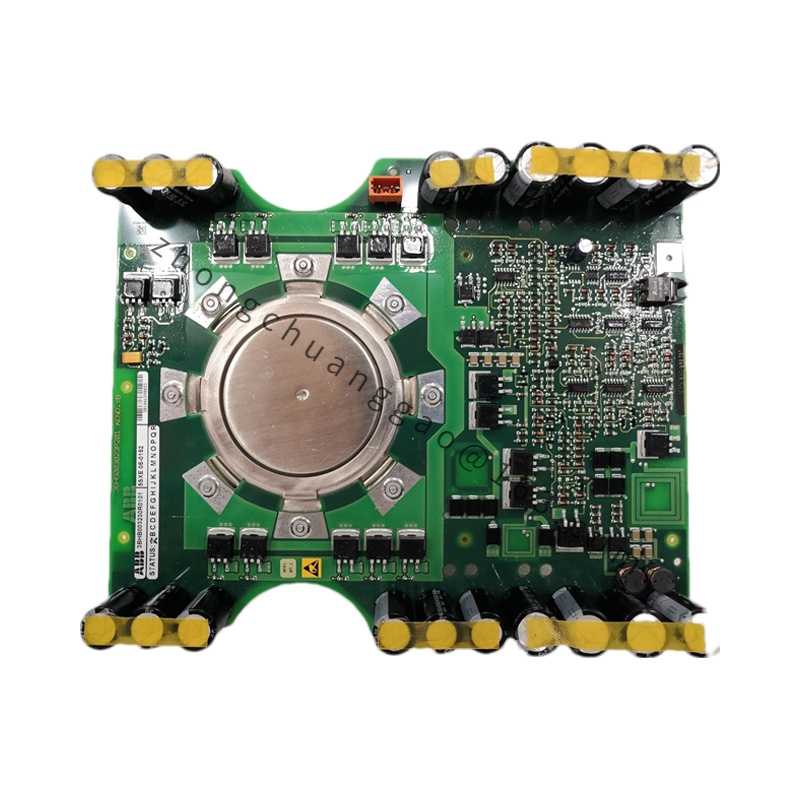
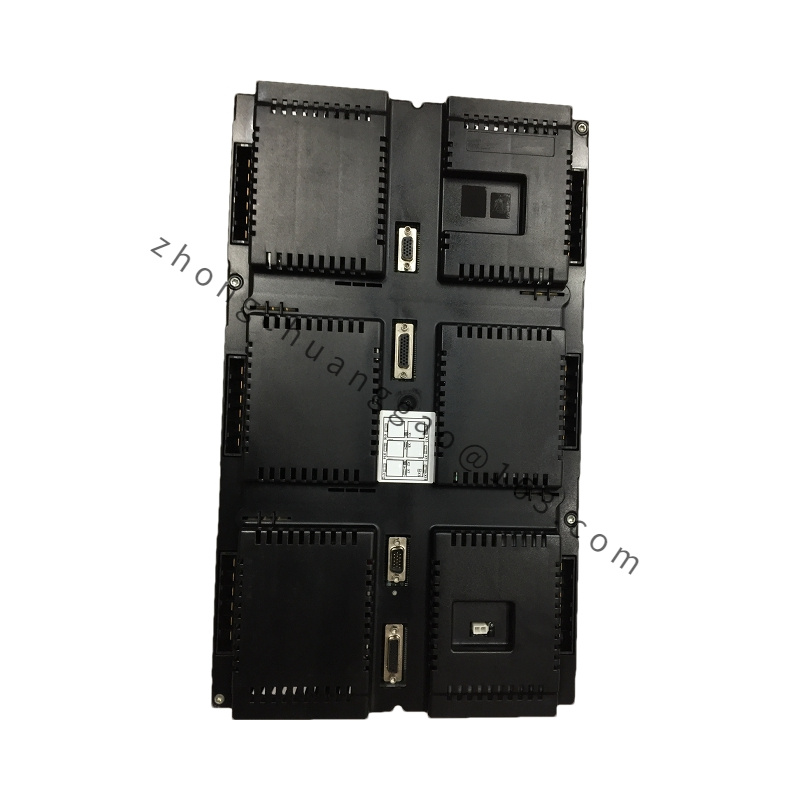












.jpg)
.jpg)