ABB PFCL201C – Pressductor PillowBlock Load Cell
- Technical Specifications
- Measurement Range: Available in multiple ranges, such as 5kN, 10kN, 20kN, and 50kN. Taking the 20kN model as an example, its measurement range is 0 – 20kN (20,000N).
- Accuracy: Generally, it can reach ±0.2%FSO, and some models can reach up to ±0.1%FSO.
- Non – linearity: ±0.2%FSO or better, and some high – end models can reach ±0.05%FSO.
- Output: Common outputs include 2mV/V, 4 – 20mA, 0 – 10V, or RS485.
- Bridge Resistance: Usually 350Ω.
- Power Supply: The input voltage range is 12 – 24V DC.
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to +80°C or -40°C to +85°C for some models.
- Humidity: 5% to 95% non – condensing.
- Protection Level: IP67, which can work in harsh environments.
- Size: Approximately 100mm×50mm×25mm.
- Weight: About 0.8kg.
- Overload Capacity: For example, the 50kN model has an overload capacity of 500kN.
Detailed content
- Function Features
- High – precision Measurement: It provides excellent accuracy and linearity, which can ensure consistent and reliable data acquisition, and is suitable for scenarios requiring precise force measurement.
- Robust and Durable: Made of high – strength stainless steel, with a potted internal structure, it can withstand shock, vibration, and harsh conditions, and has strong dust and corrosion resistance.
- Easy to Integrate: It supports a variety of mounting options and configurations, with a compact design, which is convenient to be integrated into various industrial automation systems. At the same time, it supports multiple industrial communication protocols, which is convenient for communication and connection with other devices.
- Fast Response: The response time is as short as 1ms, which can quickly respond to force changes and realize real – time monitoring and control.
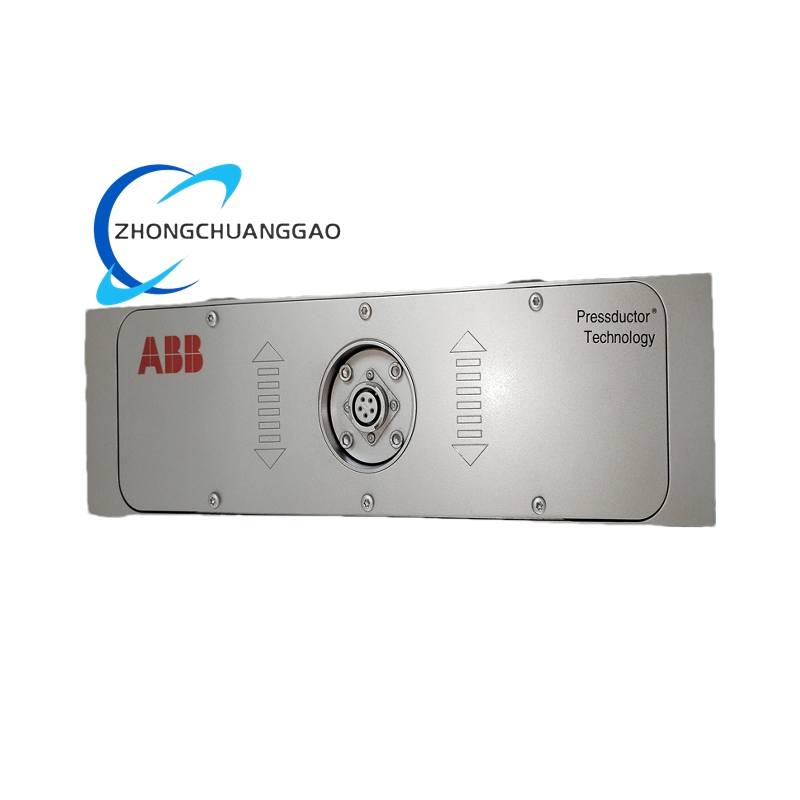

- Application Scenarios
- Industrial Automation: It is used in robots, manipulators, and assembly lines to measure and control the force during the operation process, ensuring the accuracy of operations, such as detecting the assembly pressure of engine components in the automotive manufacturing industry.
- Material Testing: It is applied to the compression strength testing of metals, plastics, composite materials, etc. In material laboratories, it can measure the yield strength and ultimate strength of materials.
- Process Control: It is used in the pressure monitoring of the chemical, petroleum, and natural gas industries, such as monitoring the pressure of pipelines and reactors to ensure the safety and stability of the production process.
- Quality Control: It is used for pressure monitoring in the production process. For example, in the food packaging industry, it can detect whether the pressure of the sealing machine meets the standard to ensure product quality consistency.
- Aerospace: It is used to monitor the hydraulic and fuel systems of aircraft and spacecraft to ensure the normal operation of key systems.
- Medical Equipment: It is used for the precise control of force in medical equipment to ensure the accuracy and safety of medical operations.









.jpg)