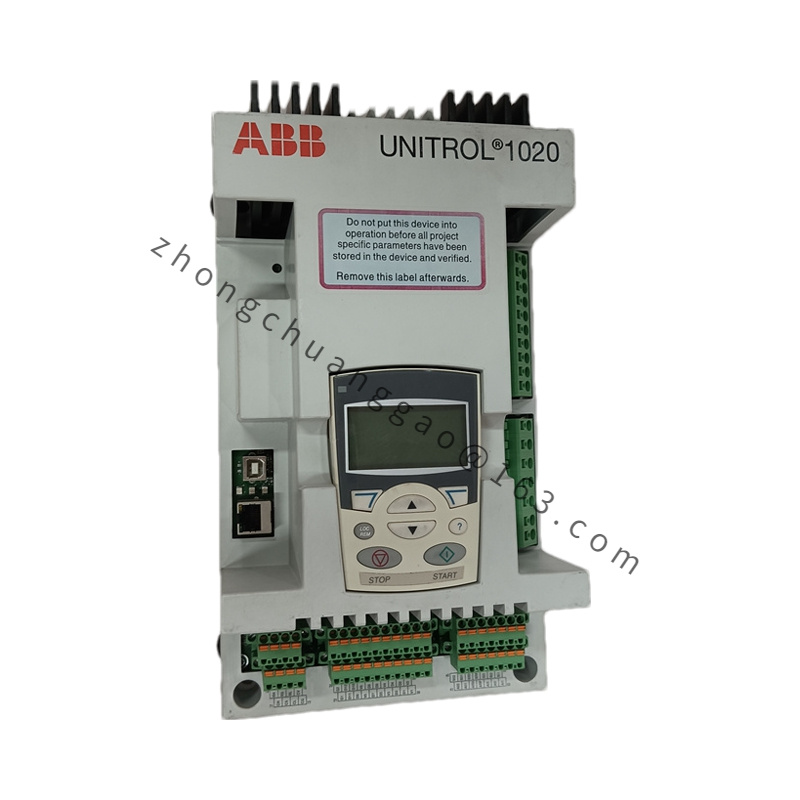
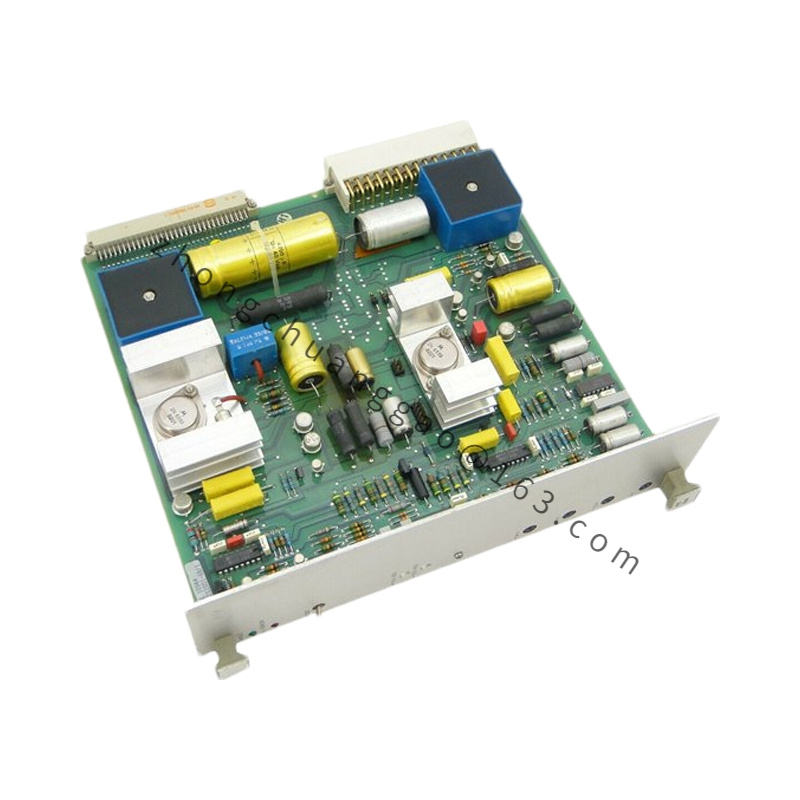
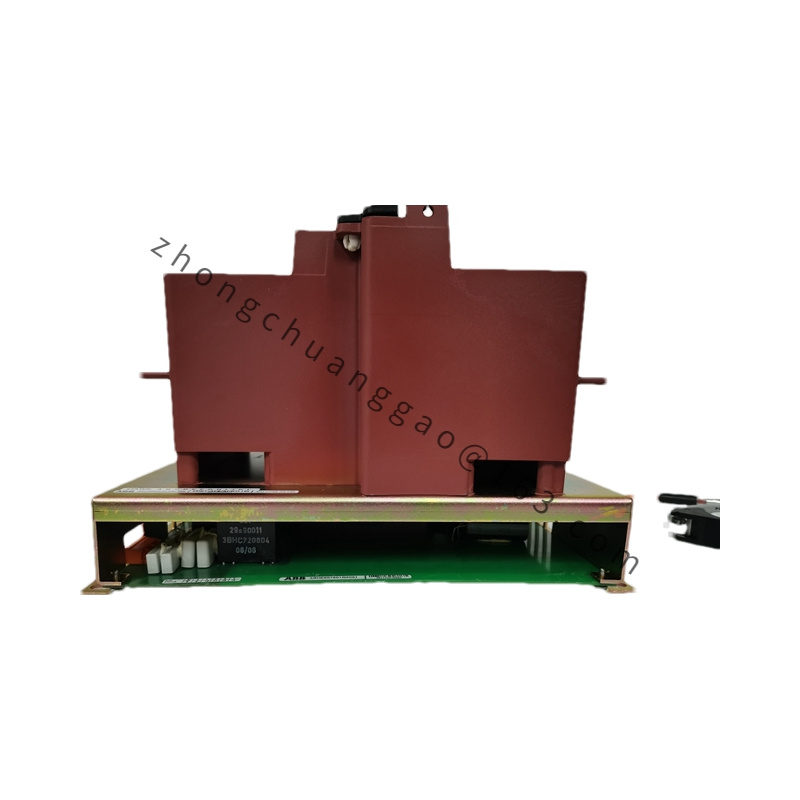
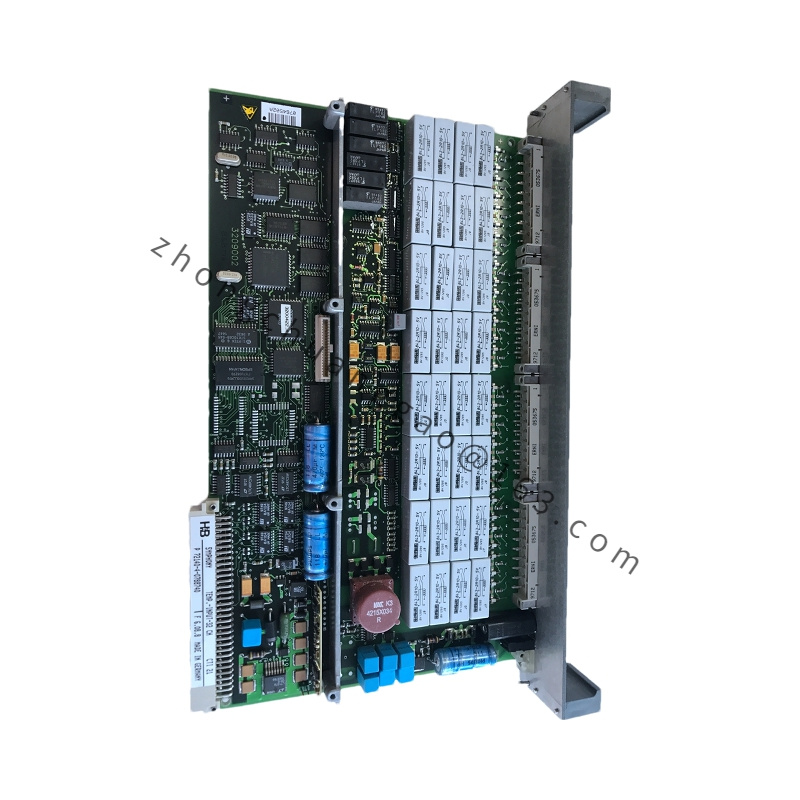
Detailed content
Technical Specifications
- Type:
- Category: Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR)
- Voltage Range:
- Input Voltage: Typically designed for operation with a wide input voltage range suitable for industrial power systems.
- Output Voltage: Adjustable to maintain stable voltage levels in the electrical system.
- Control Features:
- Regulation Type: Provides precise voltage regulation to ensure consistent power quality.
- Control Mode: Offers various control modes including manual, automatic, and adaptive to meet different operational needs.
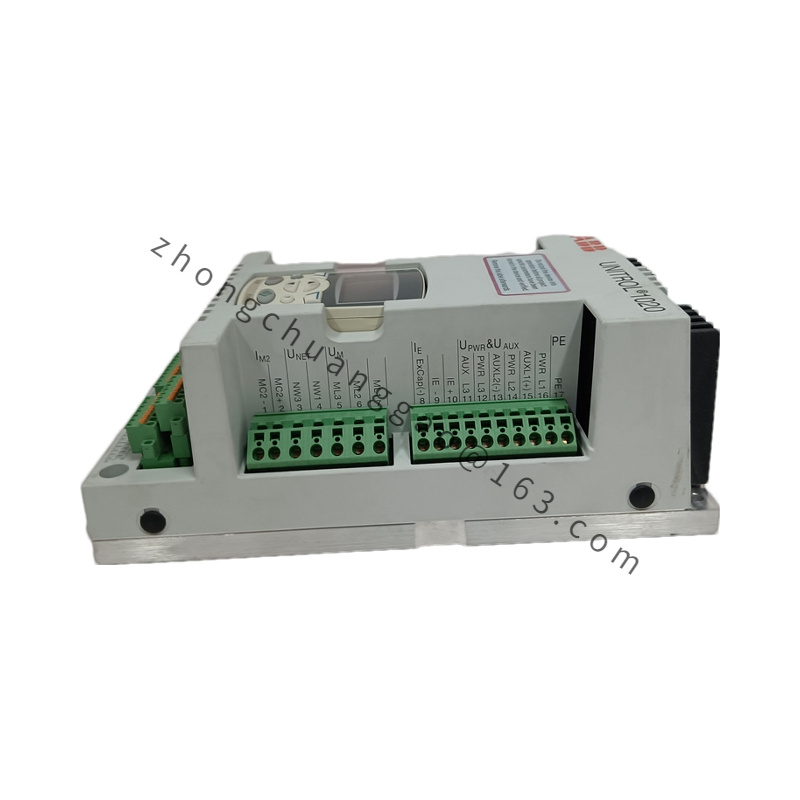
- Communication:
- Interfaces: Equipped with communication interfaces for integration with other control systems and remote monitoring.
- Protocols: Supports standard industrial communication protocols for ease of integration.
- Performance:
- Response Time: Fast response time for dynamic load changes to maintain voltage stability.
- Accuracy: High accuracy in voltage regulation to ensure optimal performance of electrical equipment.
- Environmental Conditions:
- Operating Temperature: Typically ranges from -10°C to +60°C, depending on the specific model and configuration.
- Humidity: Designed to operate in environments with relative humidity from 5% to 95%, non-condensing.
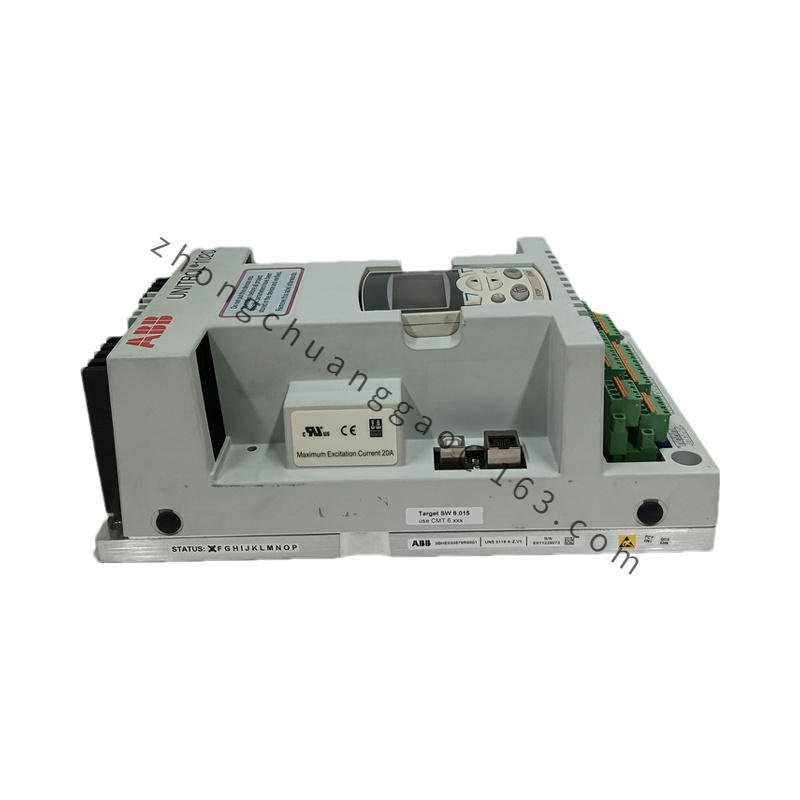
- Dimensions and Weight:
- Form Factor: Usually available in a rack-mount or panel-mount format.
- Size and Weight: Compact and lightweight design for easy installation and integration into existing systems.
Functional Features
- Voltage Regulation:
- Automatic Adjustment: Automatically adjusts the output voltage to match load demands and maintain stability.
- High Efficiency: Ensures efficient operation with minimal energy loss.
- Fault Detection and Protection:
- Protection Mechanisms: Includes various protection features such as over-voltage, under-voltage, and short-circuit protection.
- Fault Diagnostics: Provides diagnostic tools and alarms for identifying and addressing system faults.
- Flexibility and Customization:
- Adjustable Settings: Offers customizable settings for different voltage levels and control requirements.
- Modularity: Modular design allows for easy upgrades and expansion.
- Integration and Communication:
- Remote Monitoring: Capable of remote monitoring and control through communication interfaces.
- System Integration: Easily integrates with existing control systems and automation solutions.
Application Scenarios
- Power Generation:
- Usage: Used in power generation facilities to regulate the output voltage of generators.
- Benefits: Ensures stable power supply and optimal operation of generators.
- Industrial Automation:
- Application: Applied in industrial automation systems to maintain voltage stability and protect sensitive equipment.
- Advantages: Enhances the reliability and performance of industrial processes.
- Utility Power Systems:
- Function: Regulates voltage in utility power distribution systems to ensure consistent power quality.
- Effect: Improves the stability and reliability of the power supply to end-users.
- Renewable Energy:
- Role: Utilized in renewable energy systems to manage voltage output and integrate with the grid.
- Impact: Supports the effective integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid.
Additional Considerations
- Installation and Configuration: Follow ABB’s installation and configuration guidelines to ensure proper setup and operation.
- Technical Support: For detailed specifications, configuration assistance, or troubleshooting, refer to ABB’s official documentation or contact their technical support team.
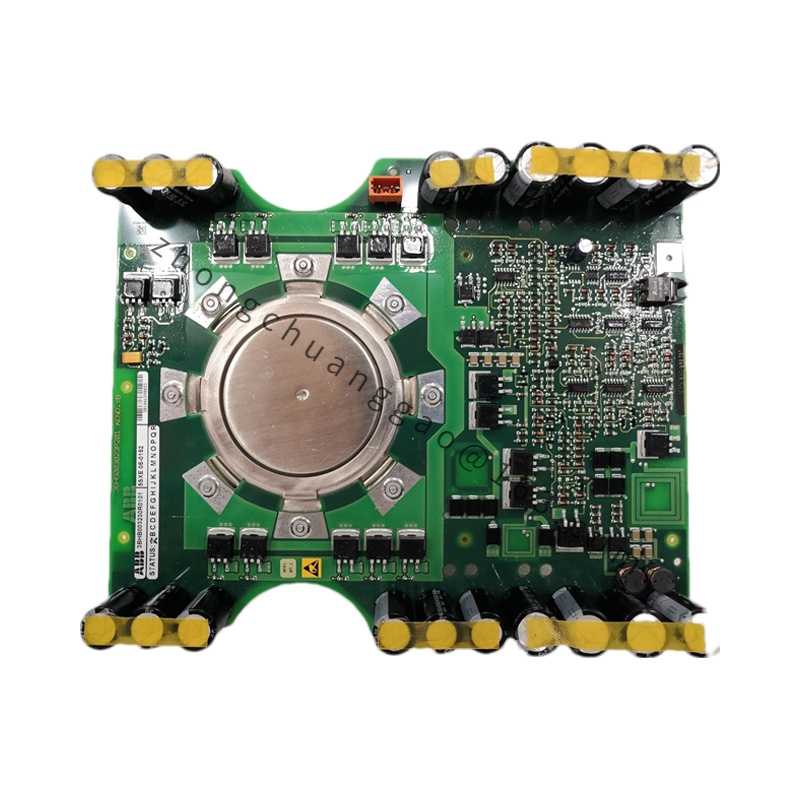
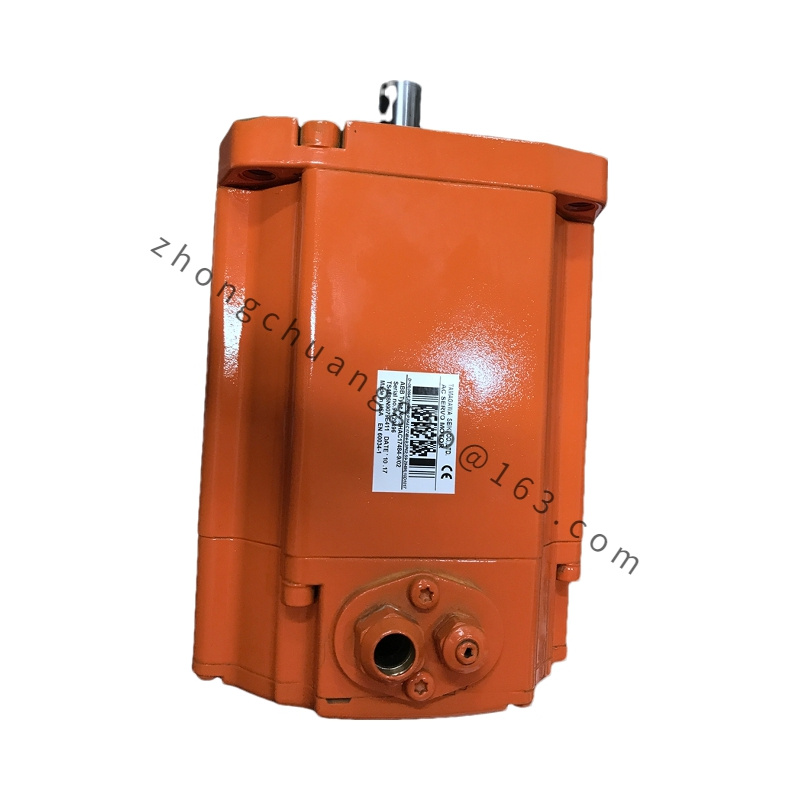
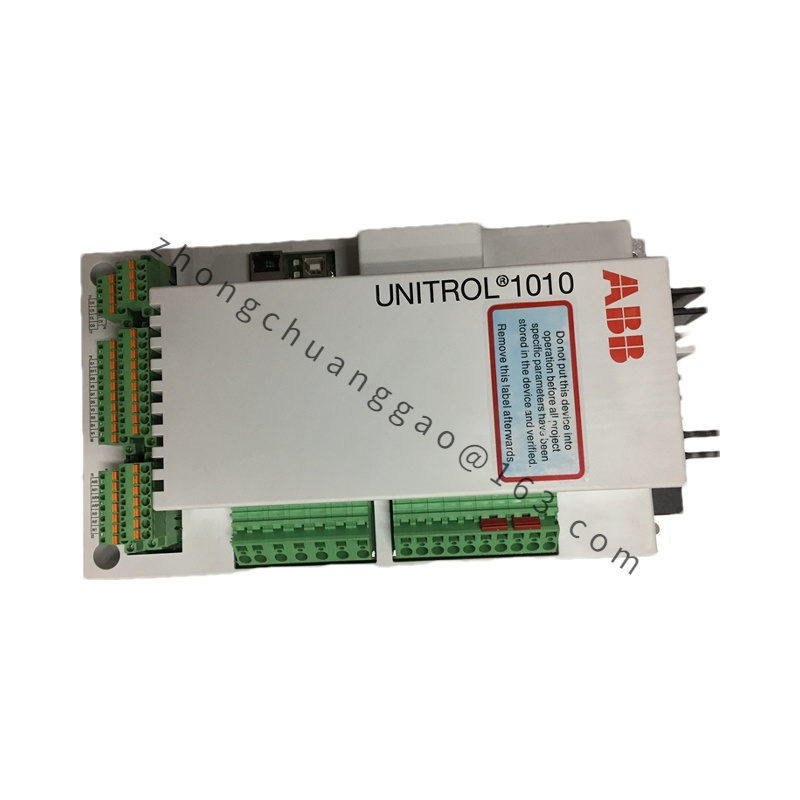











.jpg)